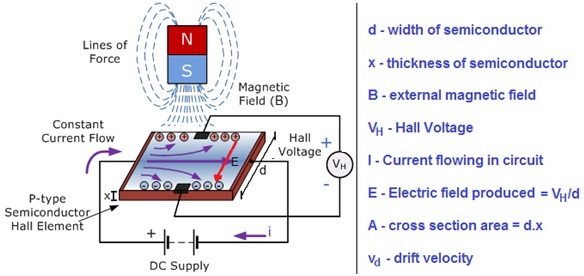
Hall Effect
When a current carrying conductor semiconductor is kept in transverse magnetic field, the charge carriers of conductors or semiconductors experience a force perpendicular to both magnetic field and current, known as Hall Effect. In Semiconductors, at equilibrium, voltage appears at semiconductor edges called Hall Voltage.
Force due to Electric Field = qE
Force due to Magnetic Field = qvdB
The simple formula for the Hall coefficient given above becomes more complex in semiconductors where the carriers are generally both electrons and holes which may be present in different concentrations and have different mobility.


No comments:
Post a Comment